What if we could teach robots to do assembly that requires spatial reasoning?
One paper from the Robotics: Perception and Manipulation (RPM) Lab at Minnesota Robotics Institute approaches solving this problem with a novel task involving distinct object pairs of 3D shapes (e.g., plus, minus, pentagon).
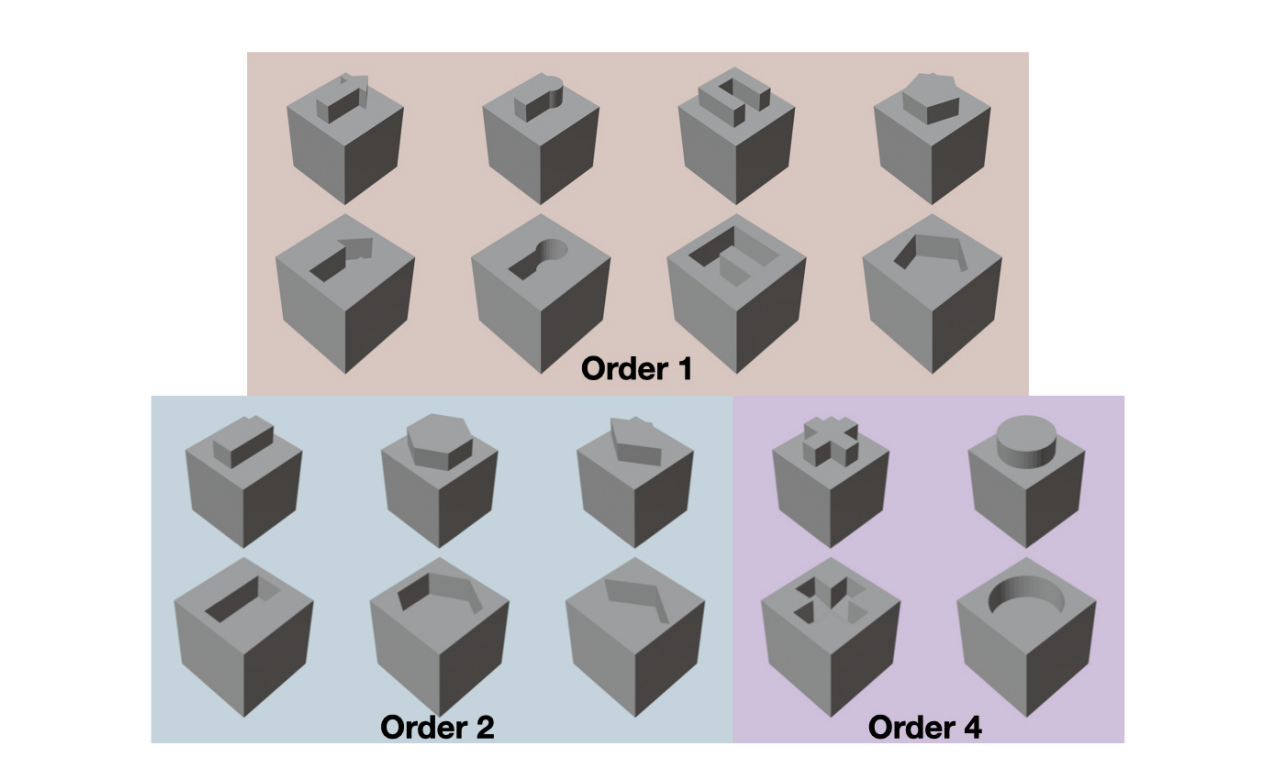
Different shape pairs used for the geometric insertion task
🎯 The Challenge:
Two robot arms must grasp different objects and figure out how to align them perfectly for insertion. When a "+" shaped peg is rotated 90°, the robot must recognize this and plan the correct alignment - pure geometric reasoning.
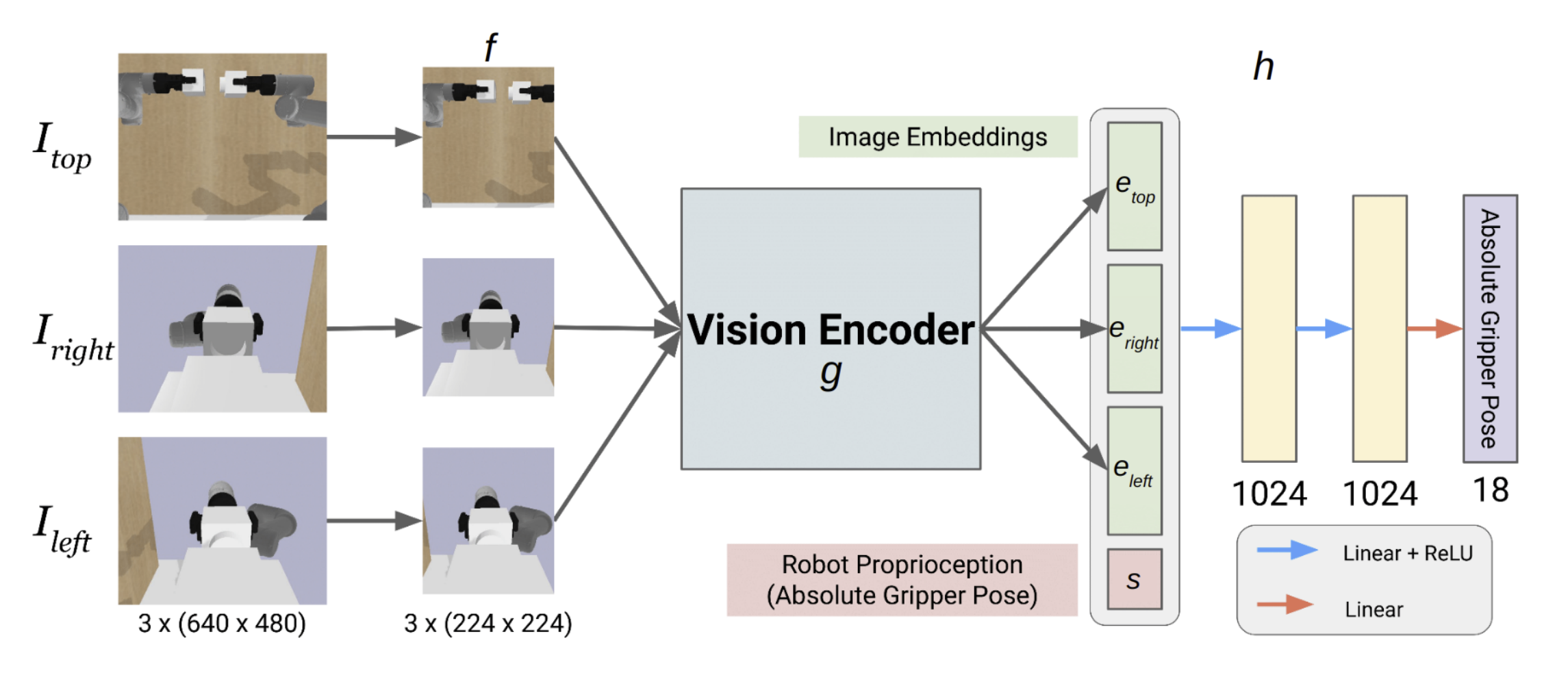
Model architecture showing the vision encoder and robot state processing pipeline
Their solution:
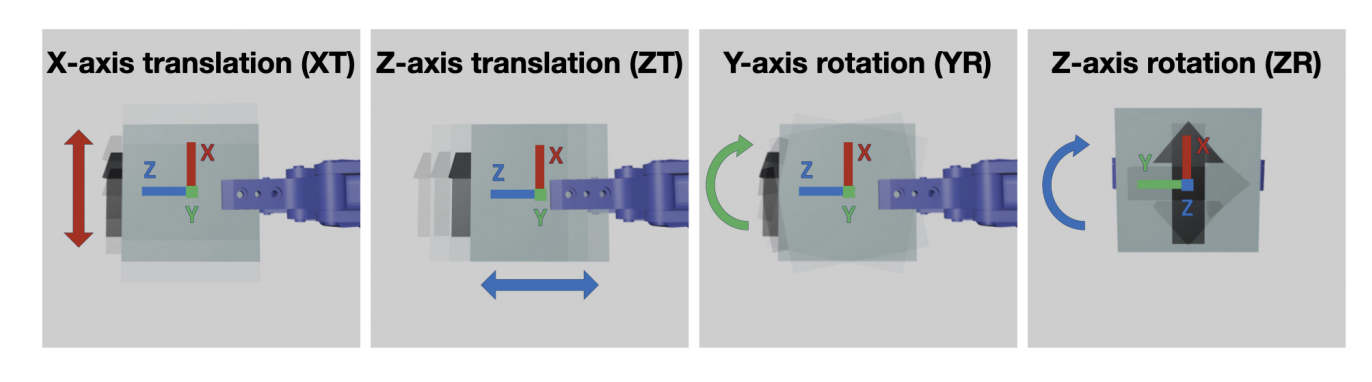
Different perturbations applied to test model robustness
🔧 How did sim2real work?
With robotics, the goal is always to build with robustness in mind. So, in order to account for real world scenarios - they add pertrubutions along different axes to inflict grasp errors.
These also include randomisation of the object pair orientation(along the Z axis), which enables the model to "actually learn spatial reasoning".
This was done across 1,000 demonstrations all run in a PyBullet simulator before being tested in the real world.
Their approach was able to get 82.5% success rate in a real world setup.
📈 What's Next:
The authors suggest DiffusionPolicy and action chunking could push accuracy even higher. Add force feedback, and we might see human-level assembly performance.
Learn More:
Paper: Evaluating Robustness of Visual Representations for Object Assembly
Task Requiring Spatio-Geometrical Reasoning
Website